Atenolol and Tinnitus: Can It Cause Ringing in the Ears?
Introduction to Atenolol and its Effects on Tinnitus
Atenolol is a medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as beta blockers. These drugs work by blocking the action of certain chemicals in the body, which helps to reduce the workload on the heart and lower blood pressure. It is commonly prescribed for conditions such as hypertension and angina. However, some people have reported experiencing tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, as a side effect of taking this medication. In this article, we will explore the relationship between atenolol and tinnitus, and discuss whether atenolol can indeed cause ringing in the ears.
Understanding Tinnitus and its Causes
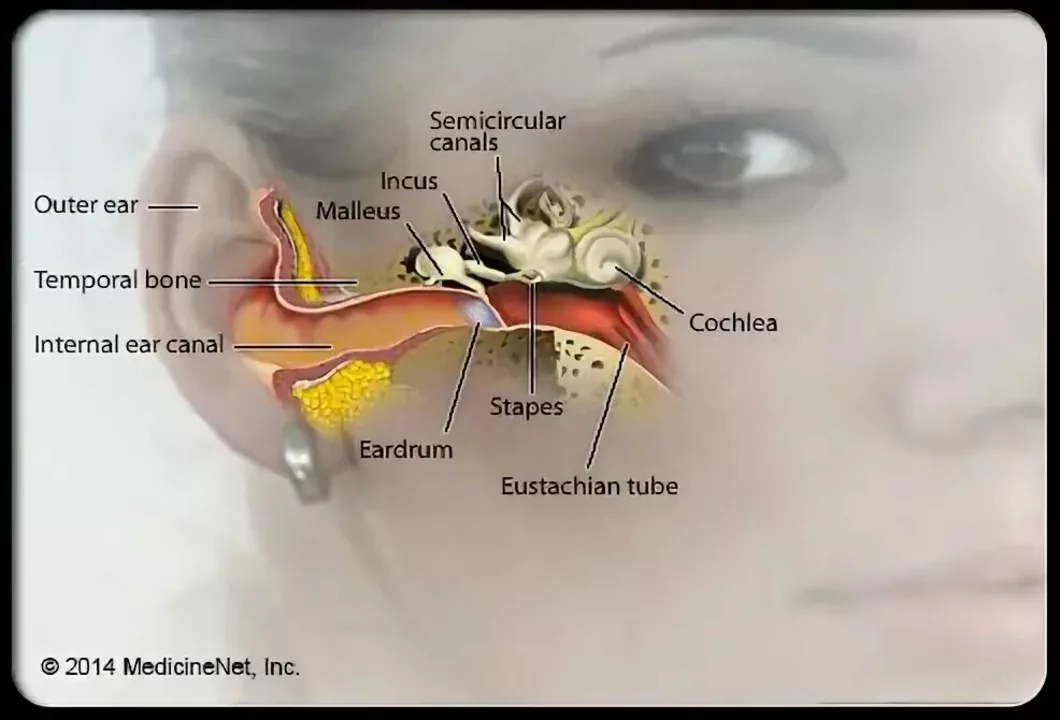
Tinnitus is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears, even in the absence of an external sound source. This condition can be temporary, intermittent, or chronic and can range from a mild annoyance to a severely debilitating problem. Tinnitus is not a disease or illness in itself, but rather a symptom of an underlying health issue.
There are numerous potential causes of tinnitus, including exposure to loud noise, ear infections, head or neck injuries, and certain medications. In some cases, it may be a result of age-related hearing loss or a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as Meniere's disease or a tumor on the auditory nerve. Although atenolol has been reported to cause tinnitus in some cases, it is important to note that there are many other potential causes for this symptom.
How Atenolol May Contribute to Tinnitus
While the exact mechanism by which atenolol may cause tinnitus is not fully understood, there are a few theories that have been proposed. One possible explanation is that atenolol, as a beta blocker, can reduce blood flow to the inner ear. This reduced blood flow may lead to a lack of oxygen and nutrients reaching the inner ear cells, which can result in damage to the delicate structures responsible for hearing and potentially cause tinnitus.
Another theory is that atenolol may directly affect the auditory system by altering the balance of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers responsible for transmitting signals between nerve cells. This disruption in neurotransmitter balance may contribute to the development of tinnitus. However, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between atenolol and tinnitus.
Managing Tinnitus Associated with Atenolol
If you suspect that your tinnitus is a side effect of atenolol, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can help determine whether your tinnitus is indeed caused by the medication and discuss alternative treatment options if necessary. In some cases, your doctor may recommend adjusting the dosage or switching to a different medication to help alleviate the tinnitus.
In addition to addressing the potential medication-related cause of tinnitus, there are several strategies that can help manage and cope with this condition. These may include using white noise machines or fans to mask the ringing, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, and seeking professional help from a therapist or support group that specializes in tinnitus management.
Conclusion: Is Atenolol a Definitive Cause of Tinnitus?
While there have been reports of tinnitus associated with atenolol use, it is important to remember that tinnitus is a complex symptom with many potential causes. It is not definitively proven that atenolol is a primary cause of tinnitus, and further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between the two.
If you are experiencing tinnitus and believe it may be related to your atenolol medication, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your concerns and explore alternative treatment options if necessary. By working closely with your doctor and employing coping strategies, you can effectively manage your tinnitus and maintain your overall well-being.




5 Comments
surender kumar
May 5, 2023 at 02:53
Oh sure, blame your ear ringing on a heart pill, because that's never been done before.
Justin Ornellas
May 5, 2023 at 03:03
While sarcasm is entertaining, the pharmacodynamics of atenolol deserve a factual appraisal. Atenolol, as a selective β1‑adrenergic antagonist, primarily reduces myocardial oxygen demand by decreasing heart rate and contractility. The drug’s effect on systemic vascular resistance is modest, but some clinicians note a mild reduction in cochlear blood flow, albeit inconsistently. A diminished perfusion pressure could theoretically compromise the stria vascularis, which maintains the ionic composition of endolymph essential for hair‑cell function. Moreover, beta‑blockers can alter the balance of catecholamines, influencing central auditory processing pathways that rely on dopaminergic signaling. Clinical reports of tinnitus associated with atenolol are sparse and often confounded by concurrent antihypertensives or ototoxic agents. The prevailing consensus in the literature is that atenolol is not a primary ototoxic drug, unlike aminoglycosides or loop diuretics. Nonetheless, a subset of patients with pre‑existing vascular insufficiency might experience heightened susceptibility. It is prudent for prescribers to monitor auditory symptoms when initiating therapy, especially in individuals with a history of ear disorders. If tinnitus emerges, a dosage adjustment or substitution with an alternative class, such as calcium channel blockers, may mitigate the complaint. Ultimately, correlation does not imply causation, and rigorous controlled studies are needed to delineate any causal link.
JOJO Yang
May 5, 2023 at 03:26
I have to say, the whole "atenolol might be the hidden villain" narrative is nothing short of theatrical tragedy – and I mean that in the most melodramatic way possible. Imagine this: a quiet evening, the world outside is calm, and suddenly a high‑pitched wail erupts from within your own skull, as if an army of violins staged a rebellion in your temporal bone. That, dear readers, is tinnitus – a relentless, tinny soundtrack that refuses to exit stage left.
Now, enter atenolol, swaggering onto the scene like a pharmaceutical James Bond, promising to tame your heart but perhaps also to turn the inner ear into a desert of oxygen. Some patients swear they felt the ringing intensify after the first dose, while others claim it was merely a coincidence, the universe's cruel joke. The scientific literature is a patchwork quilt of case reports, each thread frayed by small sample sizes and confounding variables – think noise exposure, stress, even the occasional cup of coffee that could have been the real antagonist.
One hypothesis suggests that atenolol's beta‑blocking action reduces blood flow to the cochlea, starving delicate hair cells of the nutrients they need to function properly. Another, more speculative theory, posits that the drug upsets the delicate neurotransmitter symphony in the auditory pathway, causing a dissonance that the brain misinterprets as ringing. Both ideas sound plausible, yet neither has been proven beyond a reasonable doubt, leaving us in a limbo of speculative drama.
Furthermore, let us not forget the psychological component. When you already suspect a medication might be the cause, you become hyper‑aware of any auditory anomaly, magnifying it until it dominates your consciousness like a bad actor stealing the spotlight.
So, is atenolol definitely the mastermind behind your tinnitus? Definately not – the evidence is as scattered as a broken chandelier. But if you find yourself pacing the hallway at 3 am, listening to that incessant buzz, it might be worth a chat with your doctor.
Switching to an alternative, adjusting the dose, or simply implementing sound‑masking therapy could be the denouement you need. And remember, every great story has twists, but you hold the pen to write the ending you desire.
Faith Leach
May 5, 2023 at 03:35
Ah, the classic "big pharma" smokescreen. While the drama king spins his tale, the real story is hidden in the shadows of corporate conspiracies. The moment you start questioning a medication like atenolol, you open the floodgates of suppressed research that the FDA conveniently "overlooked". They don’t want you to know that a whole class of beta‑blockers was tested for auditory side effects decades ago, and the results were buried under layers of red tape.
Listen, if you’re hearing that ringing, it’s not a coincidence – it’s a signal that the system is fighting back against chemical manipulation. The louder the tinnitus, the louder the message: stop letting these pills dictate your biology. I tell you, there’s a network of doctors paid to downplay these effects, and the patient forums are the only place where the truth surfaces.
Eric Appiah Tano
May 5, 2023 at 04:00
Hey folks, just wanted to add a balanced perspective. While anecdotal reports of tinnitus with atenolol exist, the overall incidence appears low compared to other known ototoxins. If you suspect a link, a good first step is a thorough medication review with your healthcare provider – sometimes a simple dose tweak or switch to an alternative can make a big difference. Meanwhile, sound‑masking devices, relaxation techniques, and staying hydrated are all supportive strategies that can help manage the symptom without causing alarm.