Articaine – Dental Local Anesthetic Overview
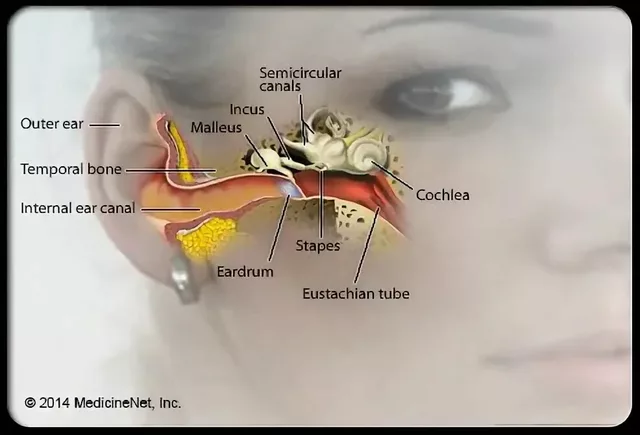
When working with articaine, a potent amide‑type local anesthetic commonly used in dentistry for short‑duration procedures. Also known as articain, it offers rapid onset and strong nerve blockade, making it a go‑to choice for many oral health professionals.
Another key player in the field is lidocaine, the oldest and most widely recognized local anesthetic in dental practice. While lidocaine provides reliable numbness, articaine’s higher lipid solubility often translates to deeper penetration and quicker effect, especially important for procedures like fillings or extractions. This relationship—articaine encompasses a broader spectrum of dental nerve block techniques—means clinicians can select the right drug based on procedure length and patient sensitivity.
How Articaine Works and Why Epinephrine Matters
Articaine requires a vasoconstrictor to prolong its action; that’s where epinephrine, a common additive that narrows blood vessels and slows anesthetic absorption comes in. By pairing articaine with epinephrine, dentists achieve a longer‑lasting numb zone, reducing the need for repeat injections. In simple terms, the drug provides the block while epinephrine extends the block—an essential semantic triple for effective pain management.
The practical side of articaine shines in its versatility. It enables quick pulp tests, smooth should‑tooth cavity work, and even minor oral surgeries with less postoperative discomfort. For patients with anxiety about needles, the faster onset means a shorter overall chair time. Studies show that articaine’s diffusion into bone tissue is superior to many alternatives, allowing successful infiltration in areas like the mandibular premolars—a spot where traditional lidocaine sometimes falls short.
Choosing the right anesthetic also depends on safety considerations. Articaine’s metabolism involves both hepatic pathways and plasma esterases, which can reduce systemic exposure compared to some agents. However, it’s still important to assess each patient’s medical history, especially regarding cardiac conditions, because the epinephrine component can affect heart rate. By understanding these nuances, dental teams can tailor anesthesia plans that balance speed, depth, and safety.
Below you’ll find a curated collection of articles that dive deeper into dental anesthetics, compare articaine with other drugs, and offer tips for safe online purchases of related medications. Whether you’re a practitioner looking for the latest evidence or a patient curious about what’s used during your next visit, the posts ahead will give you concrete, actionable information.

How Local Anesthesia Boosts Dental Treatment Success
Learn how local anesthesia works, why it matters for dental success, and the best tips to ensure pain‑free procedures.
Read More