Local Anesthesia: What It Is and Why It Matters
Local anesthesia, a technique that numbs a specific area of the body to prevent pain during procedures. Also known as regional anesthetic, it lets doctors perform minor surgeries without putting the patient to sleep. local anesthesia is the go‑to option for dental work, skin biopsies, and many outpatient procedures because it targets pain directly while keeping you alert.
Key concepts of local anesthesia
One of the most common agents is lidocaine, a fast‑acting, short‑duration numbing drug used for simple nerve blocks and surface numbing. It works by blocking sodium channels in nerve cells, which stops pain signals from traveling to the brain. Patients often feel a tingling sensation before the area goes completely numb, and the effect usually lasts 1‑2 hours—enough time for most dental fillings or minor skin procedures.
When a longer‑lasting effect is needed, practitioners may turn to bupivacaine, a potent, long‑acting local anesthetic that provides pain relief for up to 12 hours. It’s popular for regional blocks like brachial plexus or epidural anesthesia because it keeps the targeted area numb well after the surgery ends. However, the extended duration also means a higher risk of systemic toxicity, so dosages are carefully calculated based on patient weight and the area being treated.
Local anesthesia is not just about the drug—it also involves the technique of delivering the drug. Nerve block methods, such as peripheral nerve blocks or spinal anesthesia, are types of regional anesthesia that use precise needle placement to surround a nerve with the anesthetic. This approach can provide pain control for orthopedic surgeries, hand procedures, or even labor and delivery when combined with other agents.
Dental anesthesia, a specialized form of local anesthesia used in oral surgery and routine dental care is a subcategory that many patients are familiar with. Whether it’s a simple filling, a root canal, or wisdom‑tooth extraction, dentists often use a mix of lidocaine and a vasoconstrictor like epinephrine to keep the area blood‑free and extend the numbness. The goal is to make the procedure painless while allowing the patient to stay conscious and responsive.
Safety is a big part of the conversation. Common side effects include temporary numbness, mild swelling, or a brief metallic taste. Serious complications like allergic reactions or nerve damage are rare but possible, especially with higher‑dose agents like bupivacaine. Patients should always discuss medical history, current medications, and any previous reactions with their provider before undergoing a local anesthetic procedure.
If you’re looking to save money on the drugs used in these procedures, the same cost‑saving principles apply as with any prescription. Comparing generic versions of lidocaine or bupivacaine, checking reputable online pharmacies, and using discount codes can lower out‑of‑pocket expenses. Our collection below includes guides on buying cheap generic medications safely, so you can get the right anesthetic agent without breaking the bank.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into specific drugs, safety tips, and buying guides. From detailed comparisons of popular medications to practical advice on purchasing cheap generics online, these resources will help you understand the role of local anesthesia in everyday medical care and empower you to make informed decisions.
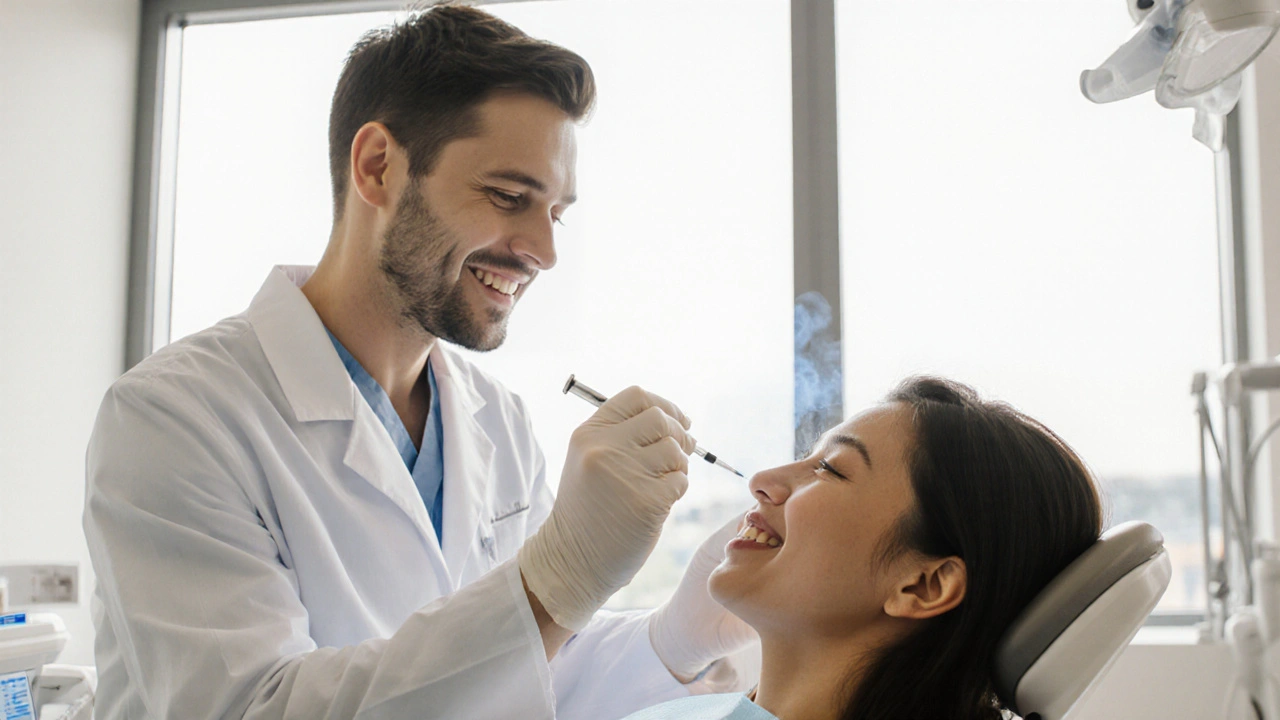

How Local Anesthesia Boosts Dental Treatment Success
Learn how local anesthesia works, why it matters for dental success, and the best tips to ensure pain‑free procedures.
Read More